India’s EV Transition: Economic Survival Addresses Climate Goals
Road transport in India contributes 12% (280Mt CO₂) of India’s yearly energy-related CO₂ emissions, with projections that depict emissions more than doubling to 580Mt CO2, contributing to a sizeable 16% of energy-related emissions by 2050 if unchecked.
To handle a part of this crisis: India aims for electric vehicles to comprise 30% of new private car sales and 75 - 80% of 2W and 3W sales by 2030, potentially reducing annual CO₂ emissions by up to 40+ million tonnes annually.
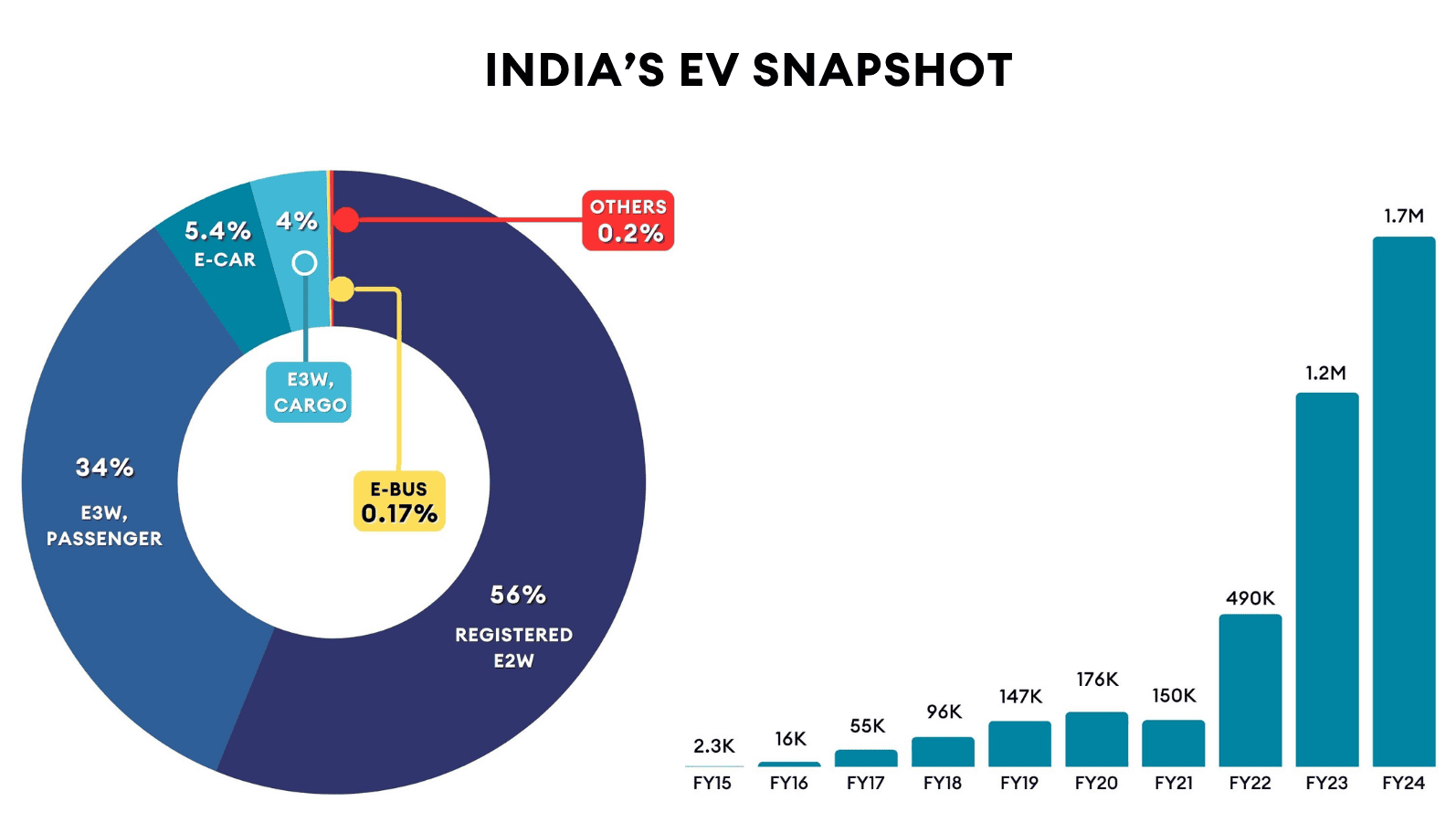
But behind this is the real reason why EV adoption by consumers or businesses in India is moving ahead - it isn’t driven by climate altruism - it’s a question of economic survival and superior economics vs the incumbents. Take a look at the numbers below
The Economic Engine Driving Adoption
1. Commercial Logistics: Profit Margins in addition to “good for the Climate”
- Food Delivery: EVs cut last-mile costs from ₹18 to ₹12 per order (33% savings).
- Gig Workers: Battery swapping adds ₹200/day earnings (vs. 4-6 hour charging downtime).
2. Personal Mobility: Poverty vs. Pragmatism
- E-Rickshaw Drivers: Earn ₹1,000/day (vs. ₹600 with petrol), repaying loans in 18 months.
- Middle Class: A ₹75,000 e-scooter costs ₹500/month in charging, less than a week’s petrol.
Why This Works:
EVs aren’t “just green”- they’re cheaper to run. A delivery rider cares more about ₹9,600/month savings than CO₂ math.
Enablers of the EV Economy: Who Profits?

1. Commercial Logistics: Profit Margins in addition to “good for the Climate”
- Problem: A gig worker loses ₹400/day waiting 4 hours to charge.
- Solution: Battery Smart (₹999/month swap plans) cuts downtime to 5 minutes, boosting earnings by 25%.
- Scale: 1,200+ swap stations added in 2023; riders now average 12 extra deliveries/day.

2. Recycling: Trash to Cash
- Problem: Replacing dead EV batteries costs ₹30,000–₹80,000, straining household savings, while India imports nearly all its lithium at an annual bill of about $2.5 billion .
- Solution: Advanced recycling recovers over 98 % of lithium and critical metals from spent batteries at 40 % below standard processing costs .
- Scale: Expanding to 300,000 t/yr by 2030 could meet 30–40 % of India’s lithium needs—saving over $1 billion in imports.
Startup Opportunities: Climate Impact Through Economics
1. Truck/Heavy Logistics Swapping
Impact: ₹3.5/km savings for fleets; Cuts 8–10 tons CO₂/year per truck.
Methodology: High-capacity battery packs + robotic swap stations for highways/mining hubs.
Impact: ₹3.5/km savings for fleets; Cuts 8–10 tons CO₂/year per truck.
Methodology: High-capacity battery packs + robotic swap stations for highways/mining hubs.
2. Recycling
Impact: 40% cheaper batteries; 90% lower mining waste vs. virgin metals.
Methodology: Recovers 95% lithium/cobalt from dead batteries via urban mining processes.
Impact: 40% cheaper batteries; 90% lower mining waste vs. virgin metals.
Methodology: Recovers 95% lithium/cobalt from dead batteries via urban mining processes.
3. Fleet Analytics
Impact: 25% higher asset utilization; Optimizes grid load during off-peak.
Methodology: AI-driven predictive maintenance + route optimization for EVs.
Impact: 25% higher asset utilization; Optimizes grid load during off-peak.
Methodology: AI-driven predictive maintenance + route optimization for EVs.
4. Circular Batteries
Impact: 50% lower lifecycle emissions; Cuts 8 tons CO₂ per recycled battery.
Methodology: Repurposes degraded batteries for grid storage, extending lifespan by 5+ years.
Impact: 50% lower lifecycle emissions; Cuts 8 tons CO₂ per recycled battery.
Methodology: Repurposes degraded batteries for grid storage, extending lifespan by 5+ years.

Siddharth Sikka,
Battery Smart Co-Founder
Note from industry stalwart:

At BlueGreen Ventures, we take pride in being early supporters of Battery Smart, with our General Partner Anup Jain (centre) leading their seed investment in 2020.
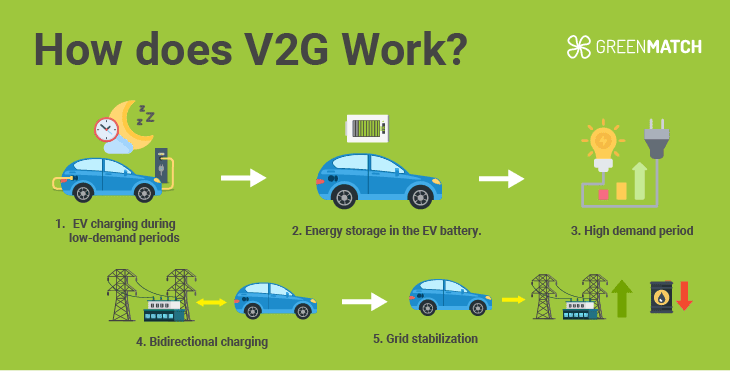
Global Lessons for India: Battery-to-Grid (V2G) – USA
Uses EVs as grid assets by compensating drivers to share idle battery power during peak demand. Execution: Utilities deploy bidirectional chargers and AI energy platforms. Impact: Stabilises grids and integrates renewables.
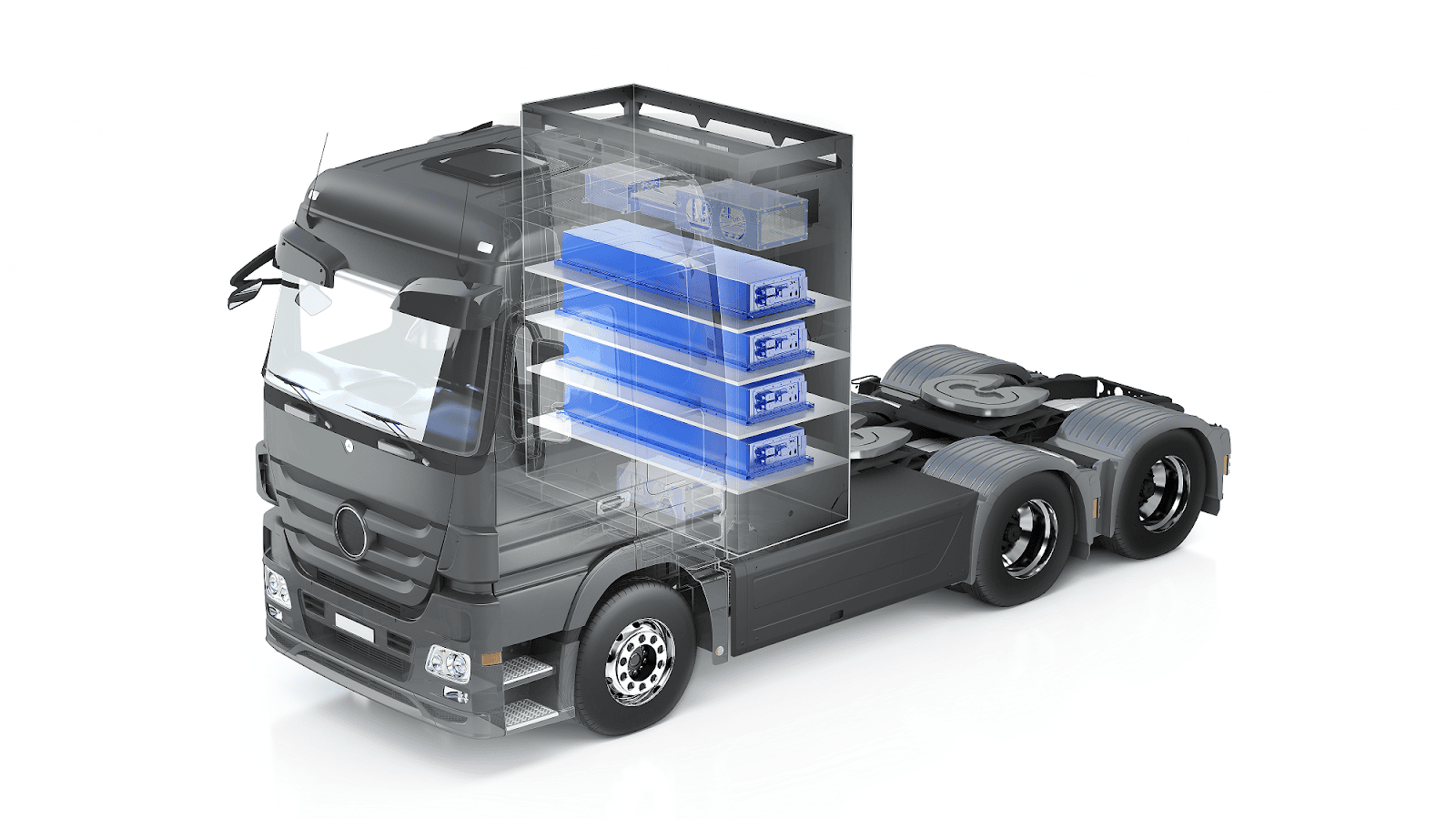
Global Lessons for India: Modular Battery Swapping – China
Solves downtime for trucks via robotic stations swapping 1.5-ton packs in 3 minutes. Execution: Highway corridors with standardised batteries. Impact: Cuts logistics costs by 25% and diesel reliance.

